Learning about Heart Sounds
Examine the following recording carefully:
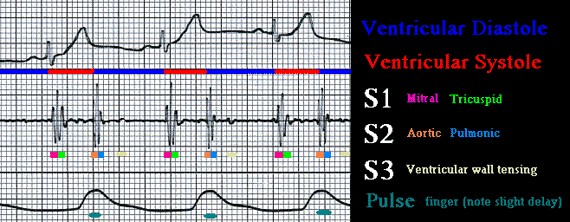
These are recorded simultaneously from a healthy 15 y.o. male "P.J." at the MCC Paramedic Lab.
To be able to appreciate and make physical diagnosis from heart sounds it is very important that the student paramedic understand the normal sequence of events in the normal heart. In addition, several terms must be understood prior to reading the following pages.
Please relate the following terms to the diagram above:
- aortic valve - A three cusp semilunar valve between left ventricle and aorta. It is the smallest valve.
- bruit (brew'-E) - A sound, heard with a stethoscope, usually created by turbulent blood flow through abnormal vessels. Not yet illustrated.
- diastole (di-as'-toe-lee) - to relax or fill with blood, when used alone (not specifying ventricular or atrial), always means ventricular diasystole.
- Erb's point - ascultatory point midway between T and P locations. (See auscultatory Landmarks below)
- early diastole - same as postsystole/postsystolic.
- gallop - Having an S3 or S4 or both. This results in sound patterns that resemble a running horse.
- late diastolic - end of diastolic period, same as presystole.
- late systole - end of systole (same a presystole time period).
- mid-diastole - middle of diastole.
- mid-systole - middle of systole.
- mitral valve - The bicuspid AV valve between the left atrium and left ventricle. It is the 2nd largest valve in the heart.
- murmur - A sound, heard with a stethoscope, usually created by turbulent blood flow through abnormal valves.
- presystole - (time) before systole, same as end diastole.
- pulmonic valve - A three cusp semilunar valve between right ventricle and pulmonic artery. It is the 2nd smallest valve.
- S1 - "Sound One" or first heart sound. The LUB in lub-dub. It is created by near simultaneous closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves.
- S2 - "Sound Two" or second heart sound. The DUB in lub-dub. It is created by near simultaneous closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves.
- S3 - Third heart sound or "ventricular gallop". Low in volume and in frequency (pitch). Heard in the early diastolic period and is normal in children. In adults >35 indicates CHF. It is NOT caused by valves, it is created by sudden tensing of the ventricular wall.
- S4 - Forth heart sound or "atrial gallop". Low in volume and in frequency. Heard in the end-diastolic period. Can indicate HTN, CAD, or AMI.
- systole (sis'-toe-lee) - to contract or eject blood, when used alone (not specifying ventricular or atrial), always means ventricular systole.
- tricuspid valve - A three cusp AV valve between right atrium and right ventricle. It is the largest valve.
| Auscultatory Landmarks | |
| Normal S1 S2 | Split S2 |
| Split S1 | Split S1 and S2 |
| S3 Gallop | S4 Gallop |
| Quadrupal Gallop | Summation Gallop |
| Systolic Murmurs | Diastolic Murmurs |
| Midsystolic Click | Practice with real sounds |

